Distribution system for TERRADISC
×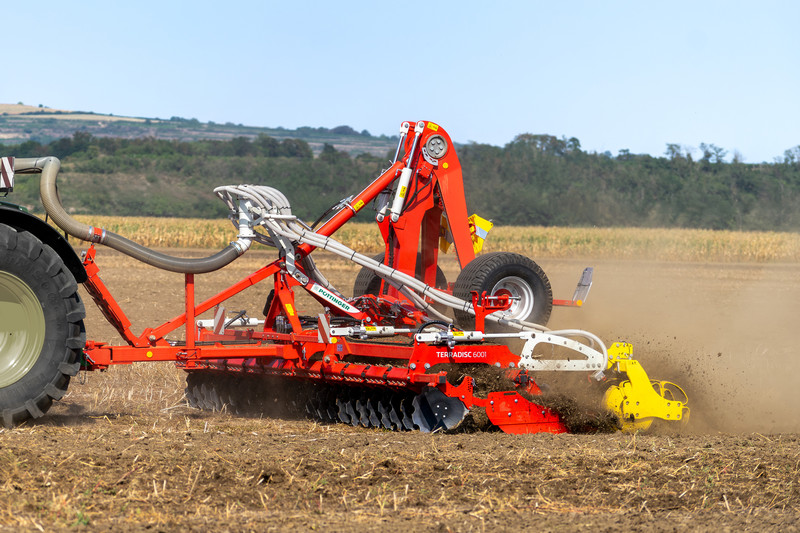
Ingenious distribution system
The tube is designed to be telescopic and is guided centrally on the main frame. The distributor head with 12 outlets is mounted on the centreline above the drawbar.
The large cross-section of 150 mm allows high quantities of fertiliser and seed to be applied in proportion to the driving speed. When the distributor head is folded out, the hoses tighten all the way to the scattering plates so that no blockages occur. As a result, the material is conveyed without obstruction, ensuring a reliable flow.
Reliable tillage tools
Large diameter, scalloped discs with a diameter of 580 mm slice into the ground and get the soil moving. The aggressive angle of the tools ensures reliable soil entry, even in the driest conditions. The TWIN ARM suspension system prevents the discs from deviating sideways on hard ground. This ensures that the whole surface is moved, which ultimately ensures uniform application of the seed material and fertiliser.

In combination with the trailed TERRADISC T disc harrows, the outlets feed the material into the flow of soil. Because it is then covered immediately, emissions during fertiliser application are prevented, while stimulating the germination of cover crops. Even at high driving speeds, precision distribution is achieved across the full width and seed and fertiliser are deposited reliably.
The angle of the distribution rail with all the outlets is adjustable, and two different placement options are described below. Depending on the application, the distribution rail can be set flatter or steeper towards the ground.
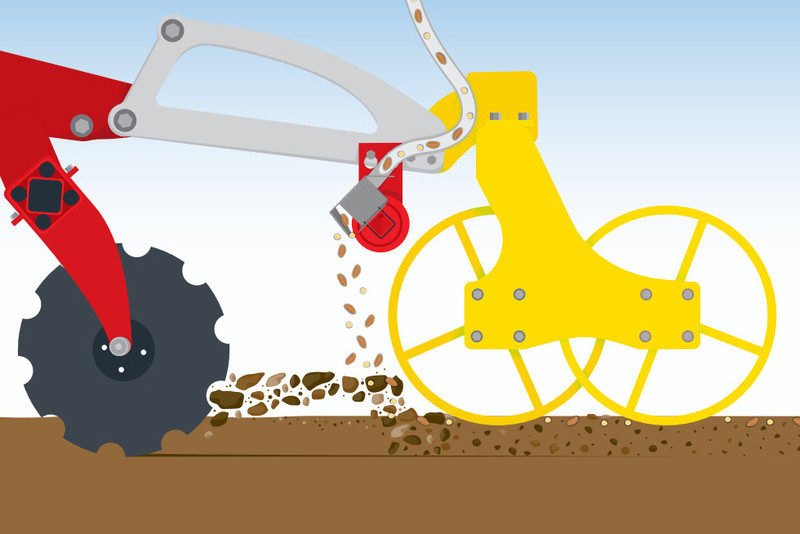
Top placement
Setting the distribution rail with the outlet diagonal to the ground feeds the material into the flow of soil. As a result, the material joins the flow of soil to be deposited on or near the surface.
This method is suitable for sowing greening or cover crop mixtures.
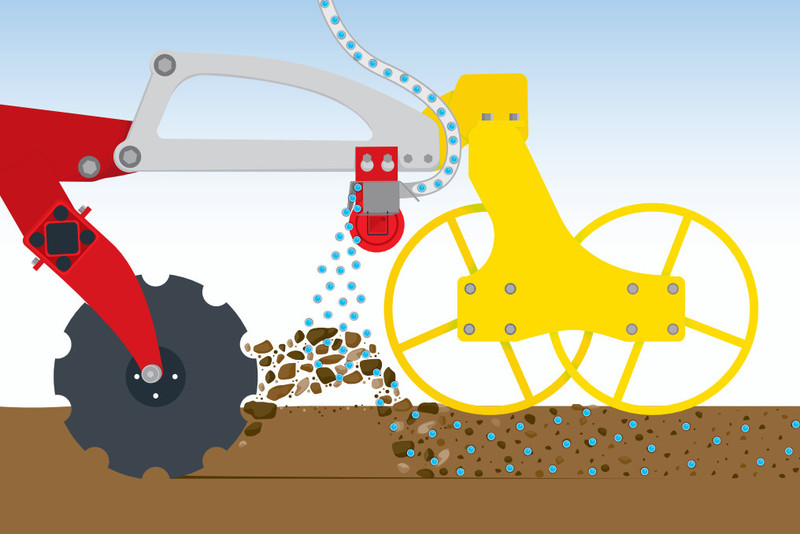
Mixed placement
By setting the distribution rail perpendicular to the ground, the material is immediately mixed into the soil below so that it is deposited across the full cultivation depth. The fertiliser and seed is therefore distributed throughout the entire cross section of soil movement.
During stubble cultivation, for example, compensatory fertilisation of potash or nitrogen can be used to accelerate the decomposition of straw.